Auto radiators can primarily differ based on their core design and materials used. Here are the primary types of Auto radiators you might come across:
1. Down-Flow and Cross-Flow Radiators:
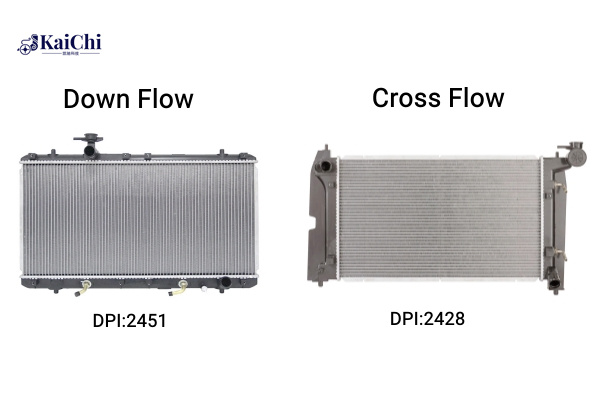
★ Down-Flow Radiator: In this common design, the coolant tanks are located at the top and bottom on the aluminum core radiator, and the coolant flows from the top tank to the bottom one, moving along with the force of gravity. While these types are very common in engine cooling system.
★ Cross-Flow Radiator: The tanks in this design are located on the aluminum core sides, and the coolant moves across from one side to the other. This design is more efficient for cooling and is more commonly found in vehicles. They can be mounted lower, more aerodynamically suitable for most of cars.
2. Single-Core and Multi-Core Auto Radiators:
★ Single-Core Radiator: These have a single row tubes running across the radiator through which the coolant passes. While simpler and less expensive than multi-core designs, they are effectively fit to small displacement engines.
★ Multi-Core Radiator: These have more than one row tube (typically two or three but even up to four), meaning there are several rows for the coolant to pass through. This design allows more coolant to be cooled at a time and subsequently provides better cooling efficiency. However, it would be more expensive and suitable for high displacement engines.
3.Materials:
★ Plastic Tanks Aluminum Core Radiator: This has become the most common type in contemporary vehicles because of manufacturing cost,weight advantages, despite the fact that they may not be as durable as all aluminum radiators.

★ All Aluminum Radiators: Most refitted vehicles use all aluminum radiators,because it's more durable, and has a good thermal conductivity,but it`s more expensive and less models compare with the aluminum core with plastic tanks radiator.

★ Copper/Brass Radiators: Older models of radiators were typically made from copper and brass. While these materials conduct heat better than aluminum, but copper radiators are heavier and more expensive.

Remember that the best radiator for a particular car can depend on many factors, including the design of the car, the climate, and the intended use of the vehicle.


